Macronutrient Comparison
Cottage cheese vs greek yogurt nutrition – Cottage cheese and Greek yogurt, two dairy powerhouses, often vie for a spot in the health-conscious consumer’s fridge. Both offer a protein punch and creamy texture, but their nutritional profiles differ subtly, impacting their suitability for various dietary needs. Understanding these differences—specifically in macronutrients—is key to making an informed choice.
Protein Content
Protein is a cornerstone of both cottage cheese and Greek yogurt, crucial for building and repairing tissues, supporting immune function, and promoting satiety. Cottage cheese, depending on the fat content, generally boasts a slightly higher protein concentration per serving than Greek yogurt. However, thetype* of protein is also important. Both contain primarily casein, a slow-digesting protein that provides a sustained release of amino acids into the bloodstream.
Greek yogurt, due to its straining process, often has a higher concentration of whey protein, a faster-digesting protein that’s quickly absorbed. This difference affects how quickly you feel full and energized after consumption.
Carbohydrate Content
Carbohydrates provide energy, but their impact on blood sugar varies. Both cottage cheese and Greek yogurt contain carbohydrates, primarily in the form of lactose, a milk sugar. Cottage cheese generally has a lower carbohydrate content than Greek yogurt, particularly in its lower-fat varieties. The difference lies in the processing; the straining process used to create Greek yogurt leaves behind some of the whey, which contains lactose.
While both contain minimal amounts of complex carbohydrates, the higher lactose content in Greek yogurt can lead to a slightly quicker rise in blood sugar for some individuals compared to cottage cheese.
Fat Content
The fat content significantly influences the overall calorie count and nutritional profile of both cottage cheese and Greek yogurt. Full-fat versions provide a richer source of calories and fat-soluble vitamins, while low-fat and nonfat options are lower in calories but may have reduced levels of certain nutrients. Both contain a mix of saturated and unsaturated fats. The type of fat present matters.
Saturated fats, found in higher quantities in full-fat varieties, should be consumed in moderation as part of a balanced diet. Unsaturated fats, on the other hand, are considered healthier fats. The fat content choice depends on individual dietary preferences and health goals.
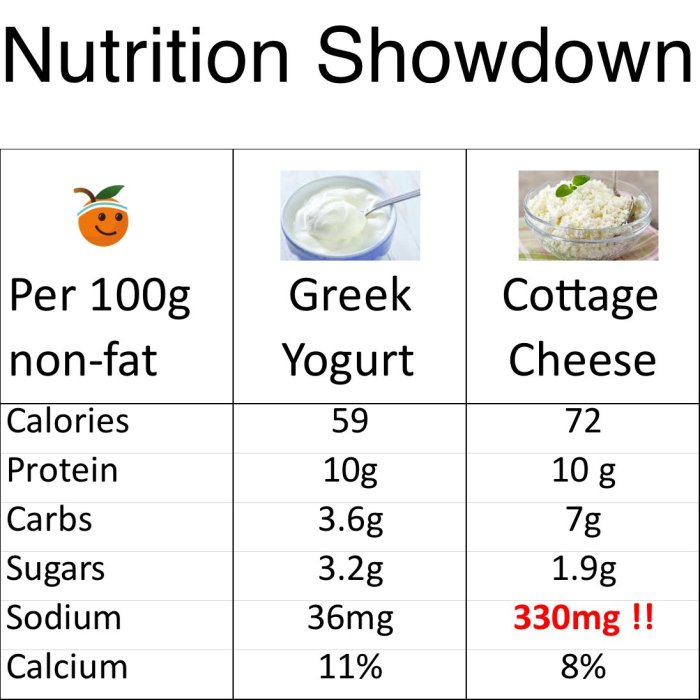
Macronutrient Comparison Table
| Food | Low-Fat (per 100g) | Full-Fat (per 100g) | Nonfat (per 100g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cottage Cheese | Protein: 12g, Carbs: 4g, Fat: 1g | Protein: 10g, Carbs: 5g, Fat: 8g | Protein: 14g, Carbs: 3g, Fat: 0g |
| Greek Yogurt | Protein: 10g, Carbs: 5g, Fat: 1g | Protein: 8g, Carbs: 6g, Fat: 10g | Protein: 12g, Carbs: 4g, Fat: 0g |
Micronutrient Profile: Cottage Cheese Vs Greek Yogurt Nutrition
Beyond the macronutrients, both cottage cheese and Greek yogurt offer a compelling array of micronutrients vital for optimal health. While both are nutritional powerhouses, their micronutrient profiles reveal subtle yet significant differences that can influence your dietary choices. Understanding these nuances allows for a more informed selection based on individual nutritional needs.These differences aren’t simply about numbers on a label; they represent distinct contributions to your overall well-being.
For example, the varying levels of certain vitamins can impact energy production, immune function, and even bone health. Let’s delve into the specifics.
Vitamin and Mineral Content Comparison
Cottage cheese and Greek yogurt boast a diverse range of vitamins and minerals. Cottage cheese is a good source of riboflavin (vitamin B2), crucial for energy metabolism and healthy skin. It also provides selenium, an antioxidant that protects cells from damage. Greek yogurt, on the other hand, often shines with higher levels of calcium and probiotics, beneficial for gut health and bone density.
Both foods contribute to your intake of phosphorus, essential for strong bones and teeth, and potassium, an electrolyte that supports healthy blood pressure. However, the quantities of these nutrients can vary depending on factors such as the brand, fat content, and any added ingredients.
Calcium and Potassium Content
The comparison of calcium and potassium in cottage cheese and Greek yogurt highlights the importance of considering these minerals within a balanced diet.
- Calcium: Greek yogurt generally contains significantly more calcium than cottage cheese. Calcium is the cornerstone of strong bones and teeth, and plays a vital role in muscle function and nerve transmission. A deficiency can lead to osteoporosis and other health problems.
- Potassium: While both foods contribute to potassium intake, the difference is less pronounced than with calcium. Potassium is crucial for maintaining healthy blood pressure and regulating fluid balance in the body. Adequate potassium intake is associated with a reduced risk of stroke and heart disease.
Vitamin B12 Content and Significance
Vitamin B12 plays a crucial role in nerve function, red blood cell formation, and DNA synthesis. A significant difference lies in the vitamin B12 content of these two dairy products. Greek yogurt, particularly full-fat varieties, often contains higher levels of vitamin B12 than cottage cheese. This is partly due to the fortification practices of many yogurt manufacturers.
A deficiency in vitamin B12 can lead to pernicious anemia, characterized by fatigue, weakness, and neurological symptoms. Therefore, the higher B12 content in many Greek yogurts can be a considerable advantage for individuals at risk of deficiency, such as older adults or those following strict vegetarian or vegan diets.
Digestive Health Aspects

The impact of cottage cheese and Greek yogurt on your digestive system is a complex interplay of factors, primarily revolving around lactose content, probiotic presence, and individual sensitivities. Both offer potential benefits, but understanding their nuances is key to choosing the best option for your gut health.
Lactose intolerance, a common digestive issue, significantly influences the choice between these two dairy products. The amount of lactose present in each, along with the speed of digestion, affects how well your body processes it. Probiotics, live microorganisms, play a crucial role in maintaining a healthy gut microbiome, contributing to better digestion and overall well-being. The types and quantities of these beneficial bacteria vary between cottage cheese and Greek yogurt, influencing their impact on gut health.
Lactose Content and Digestion
Cottage cheese generally contains less lactose than Greek yogurt due to the whey separation process during its production. This makes it a potentially better choice for individuals with mild lactose intolerance. However, even with lower lactose, some individuals may still experience discomfort. Greek yogurt, while typically containing more lactose, often undergoes straining, which can slightly reduce lactose levels compared to regular yogurt.
The lactose content can also vary significantly depending on the brand and manufacturing process. Managing lactose intolerance often involves consuming smaller portions, choosing low-lactose options, or using lactase enzyme supplements.
Probiotic Content and Gut Microbiome
Both cottage cheese and Greek yogurt can contain probiotics, though their presence and types vary widely depending on the brand and whether live cultures have been added. Greek yogurt, particularly those explicitly marketed as containing live and active cultures, often boasts a higher concentration of beneficial bacteria such as
- Lactobacillus* and
- Bifidobacterium* strains. These probiotics contribute to a balanced gut microbiome by aiding in digestion, producing beneficial compounds, and potentially suppressing harmful bacteria. Cottage cheese, while sometimes containing probiotics, typically has a lower concentration than Greek yogurt.
Potential Digestive Issues and Mitigation Strategies
Consuming either cottage cheese or Greek yogurt can lead to digestive issues in some individuals. For those with lactose intolerance, bloating, gas, and diarrhea are common after consuming dairy. Reducing portion sizes, opting for low-lactose versions, or taking lactase supplements can help alleviate these issues. Furthermore, some individuals may experience discomfort from the high protein content of both foods, leading to feelings of fullness or indigestion.
In these cases, consuming smaller amounts or incorporating them into meals instead of eating them alone might be beneficial. In rare cases, individuals might have an allergic reaction to dairy proteins, manifesting as more severe symptoms requiring medical attention.
Choosing between cottage cheese and Greek yogurt often boils down to personal preference, but understanding the nutritional differences is key. For those watching their fat intake, exploring the specifics of nonfat cottage cheese nutrition can be particularly insightful. Ultimately, the “better” choice in the cottage cheese vs. Greek yogurt debate depends on your individual dietary needs and goals.
Impact of Cottage Cheese and Greek Yogurt on Digestive Health, Cottage cheese vs greek yogurt nutrition
| Food | Potential Benefits | Potential Drawbacks | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cottage Cheese | Lower lactose content (potentially), good source of protein | May still contain lactose, lower probiotic content | Choose low-lactose options, consume in moderation, consider lactase supplements |
| Greek Yogurt | Often higher probiotic content, good source of protein and calcium | Higher lactose content (potentially), can cause discomfort for some | Choose low-lactose options, consume in moderation, consider lactase supplements |
Cost and Availability

The battle of the breakfast (or snack!) champions isn’t just about protein and probiotics; it’s also a matter of budget and convenience. Choosing between cottage cheese and Greek yogurt often hinges on factors beyond nutritional content, leading us to explore the often-overlooked aspects of cost and accessibility. Let’s delve into the economic and logistical realities of procuring these protein powerhouses.
A direct comparison of cottage cheese and Greek yogurt prices reveals a fascinating dynamic. While the price per unit of protein can fluctuate depending on brand, fat content, and retailer, cottage cheese frequently emerges as the more budget-friendly option. This isn’t always the case, however, as certain premium Greek yogurts can undercut the cost of higher-fat cottage cheese varieties.
Availability also plays a crucial role; readily accessible options in one region might be a rarity in another.
Price Comparison per Unit of Protein
Calculating the exact cost per gram of protein requires checking current prices at your local stores. However, a general observation suggests that, on average, cottage cheese often provides a higher protein content per dollar compared to Greek yogurt. This is particularly true for lower-fat varieties of Greek yogurt, which often command a higher price point despite a lower protein content per serving.
For example, a 16-ounce container of low-fat cottage cheese might cost around $2.50 and contain 40 grams of protein, while a similarly sized container of low-fat Greek yogurt could cost $3.50 and contain only 30 grams of protein. This illustrates a potential cost advantage for cottage cheese in this scenario.
Retail Availability and Regional Differences
The ease with which you can find cottage cheese and Greek yogurt varies significantly depending on your location and the type of store you visit. Major supermarkets generally stock both products, but smaller stores or those in more rural areas may have limited selections. Regional preferences also play a part. In some regions, cottage cheese might be more commonly consumed and therefore more widely available, while in others, Greek yogurt holds the reign.
For instance, Greek yogurt enjoys significant popularity in the Northeastern United States, while cottage cheese might be more prevalent in certain parts of the Midwest.
Factors Influencing Price
Several factors contribute to the fluctuating prices of both cottage cheese and Greek yogurt. Understanding these factors allows for a more informed purchasing decision.
- Brand Recognition: Established brands often command higher prices due to their marketing and perceived quality.
- Fat Content: Full-fat varieties are generally more expensive than low-fat or non-fat options.
- Packaging and Size: Larger containers may offer a better price per unit, but this needs to be considered against storage capacity and consumption rates.
- Production Costs: Fluctuations in milk prices and other production inputs directly impact the final cost of the product.
- Retailer Markups: Different retailers apply varying markups, influencing the final price paid by the consumer.
Factors Affecting Availability
The availability of these dairy products is influenced by several interconnected factors.
- Seasonal Milk Production: Milk production varies seasonally, potentially affecting the availability and cost of both cottage cheese and Greek yogurt.
- Regional Demand: High demand in a particular region can lead to shortages or higher prices.
- Transportation and Logistics: Efficient distribution networks are essential for ensuring consistent availability, especially in more remote areas.
- Production Capacity: The overall production capacity of dairy processors influences the supply available to meet market demand.
- Consumer Preferences: Shifting consumer preferences can affect the production and distribution focus of dairy companies.
FAQ Overview
Can I eat cottage cheese and Greek yogurt daily?
Moderation is key. Daily consumption is generally safe for most, but excessive intake could lead to digestive discomfort or exceed daily dairy recommendations.
Are there lactose-free versions of cottage cheese and Greek yogurt?
Yes, many brands offer lactose-free varieties, catering to individuals with lactose intolerance.
Which is better for weight loss: cottage cheese or Greek yogurt?
Both can support weight loss due to their high protein content, promoting satiety. The best choice depends on your overall caloric intake and macronutrient targets.
How should I store cottage cheese and Greek yogurt?
Refrigerate both in airtight containers to maintain freshness and prevent spoilage.
